Beauty of digital marketing always stays in its techniques and channels. Among these strategies, Pay-Per-Click (PPC) marketing stands out due to its remarkable ability to drive quick results. But what is it, why should you use it, and how does it work? Dive in to explore more about this cost-effective digital marketing strategy.
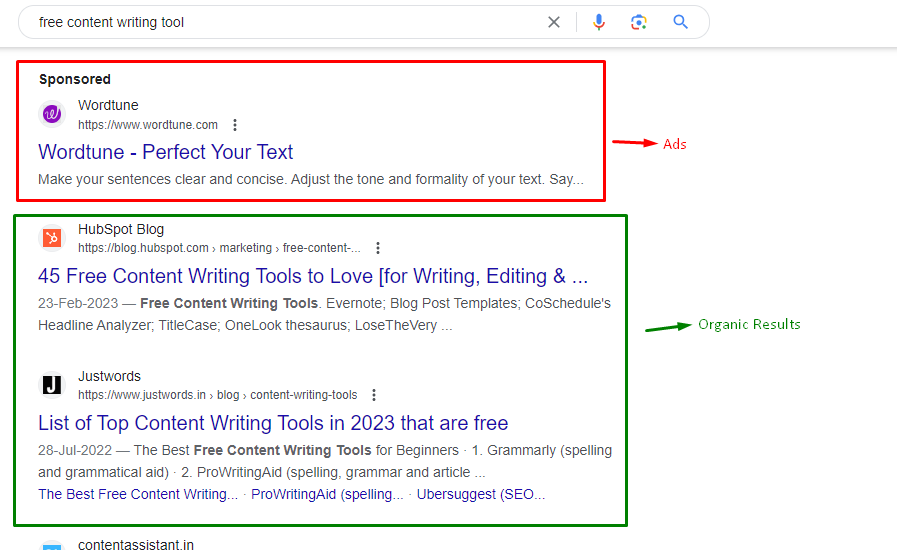
What is PPC Marketing?
PPC, an acronym for Pay-Per-Click, is an internet marketing model where advertisers pay a fee each time one of their ads is clicked. Instead of earning visits organically, businesses can buy visits to their site. PPC is closely associated with first-tier search engines like Google Ads and Bing Ads. As per reports 79% brands agree that ppc is great revenue drivver for their business refer to Start Up Bonsai ppc stats blog.
Why You Should Leverage PPC Advertising
While marketers always mention to leverage PPC in their digital marketing strategy. But why you should employee ppc advertising? Following are the reasons
1. Quick Results
Unlike SEO efforts, which take time to reflect, PPC can provide immediate results as you’re directly paying for visits to your site.
Also read – SEO vs PPC: Who is Winning the Powerful Debate
2. Budget Control
You can set your budget according to your needs. You’re only charged when a user actually clicks on your ad.
3. Targeted Advertising
PPC allows you to target your audience based on demographics, location, keywords, interests, and more.
4. Measurable ROI
With PPC, everything is measurable. You can easily track which ads, keywords, and placements are driving the most return.
How PPC Works for Beginners
Now we have covered “what” and “why” part of PPC advertising, let’s jump into “how” part of PPC campaigns. Let go deep about types of campaigns and bidding strategies.
Types of Campaigns
There are several types of PPC campaigns, including search campaigns, display campaigns, shopping campaigns, video campaigns, and app campaigns. The choice depends on your business goals.
1. Search Campaigns
These are the most common type of PPC campaigns. Whenever a user queries a keyword in a search engine like Google, ads related to that keyword might appear above the organic results.
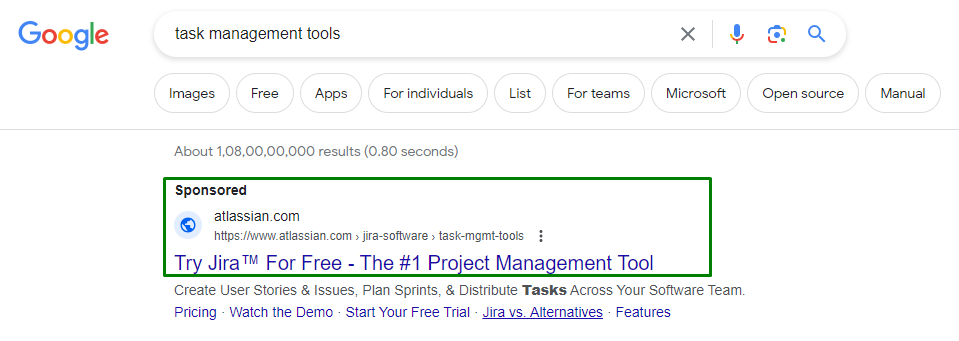
Advantages:
- High intent: Users are actively searching for something, meaning they might be closer to making a purchase or conversion.
- Vast reach: Search engines process billions of searches per day.
2. Display Campaigns
Display campaigns allow your ads to appear on a variety of websites across the internet, not just on search engine results. These ads can be in the form of banners, infographics, or interactive content.
Advantages:
- Visual appeal: You can use eye-catching visuals to attract potential customers.
- Brand awareness: Display ads are excellent for promoting brand recognition.
3. Shopping Campaigns
Primarily used by e-commerce businesses, shopping campaigns showcase products directly in search engine results. They include product images, prices, and store names.
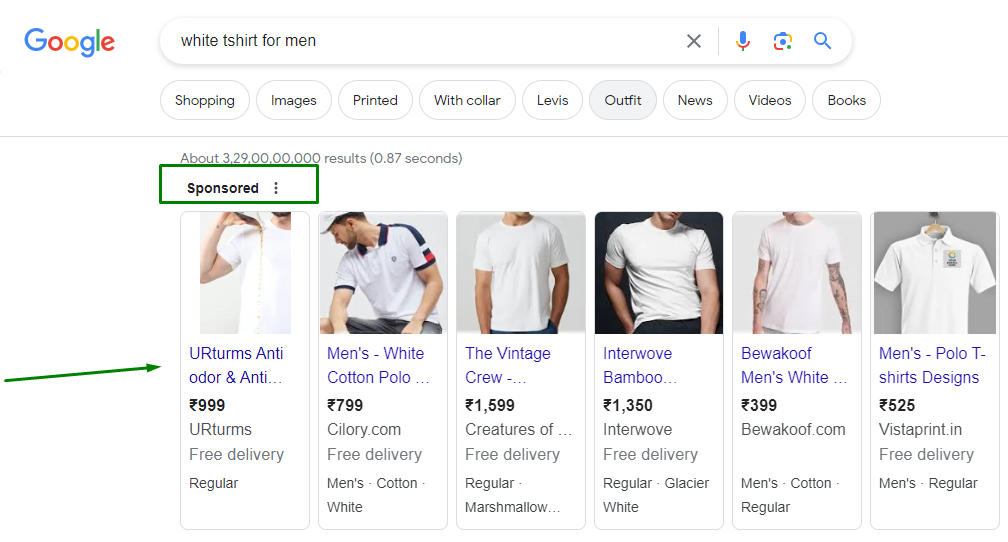
Advantages:
- Product-focused: Directly displays products to potential buyers.
- Enhanced visibility: Combines image and text for a standout ad presence.
4. Video Campaigns
Video campaigns allow businesses to run video ads on platforms like YouTube. They can be short clips before a user’s chosen video plays, long-form content, or even non-skippable video ads.
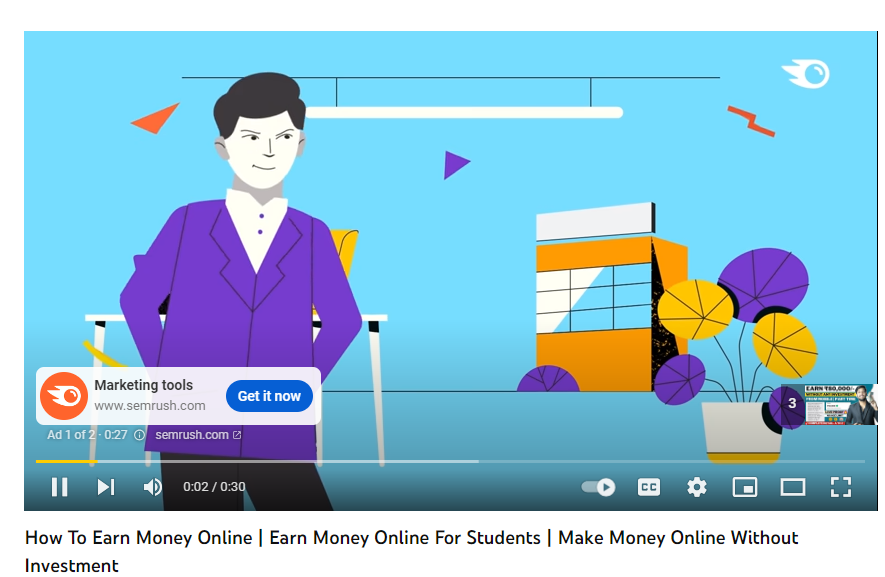
Advantages:
- Engaging: Videos can often convey a message more effectively than text or images alone.
- Diverse formats: From short clips to longer informational videos, you can experiment with various video lengths and styles.
5. App Campaigns
App campaigns are designed for businesses looking to promote their mobile apps. These ads can appear across Google’s properties, including Search, Play Store, YouTube, and the Display Network.

Advantages:
- Mobile-focused: Directly targets mobile device users.
- Broad reach: Reaches potential users across multiple platforms.
6. Remarketing/Retargeting Campaigns
This type of campaign targets users who have previously visited your website or engaged with your brand but did not make a purchase or fulfill a desired action. By displaying ads to these users as they browse other websites, you can remind them of their interest and potentially bring them back to complete the conversion.

Advantages:
- Higher conversion potential: Targets users already familiar with your brand or product.
- Personalized touch: You can customize ad content based on the user’s previous interactions with your website.
7. Local Service Ads Campaign
These ads are specifically designed for local businesses offering services like plumbing, cleaning, or repairs. They show up when users search for specific local services and include reviews, business hours, and more.
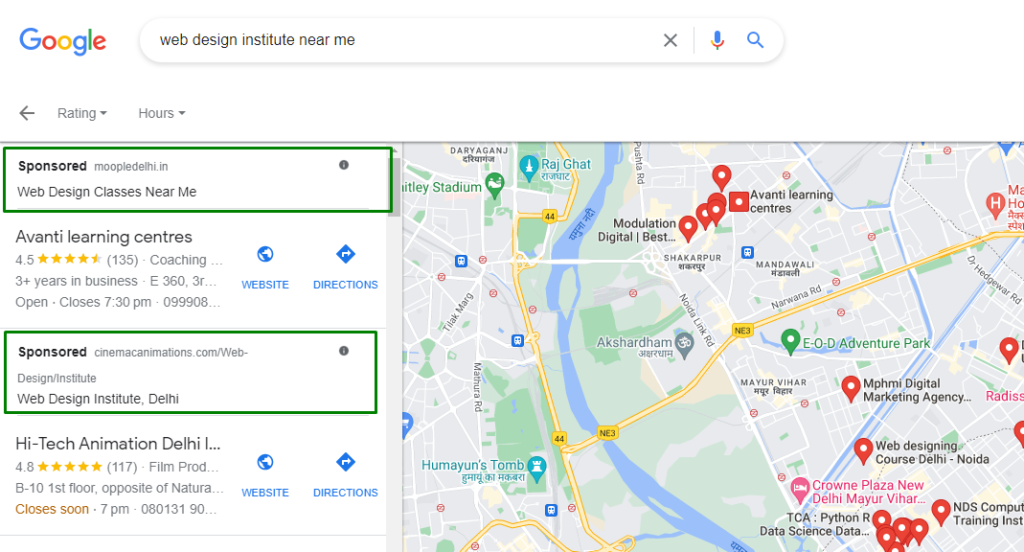
Advantages:
- Highly targeted: Focuses on users searching for a particular service in a specific location.
- Trust-building: Features reviews and ratings to establish credibility.
8. Call Only Campaigns
Call Only campaigns are designed to encourage users to call a business directly from the ad. These ads display prominently on devices that can make calls, bypassing the need for a landing page.

Advantages:
- Immediate Engagement: Eliminates extra steps for users, leading to faster and more direct communication.
- Higher Conversion Potential: By targeting users ready to make a call, there’s a higher likelihood of capturing high-intent leads or sales.
9. Performance Max Campaigns
Definition: A Google Ads campaign type, Performance Max leverages machine learning to auto-optimize ad placements across all of Google’s channels based on set goals.
Advantages:
- Automated Efficiency: Simplifies campaign management, reducing manual effort in ad placement optimization.
- Broad Reach: Taps into all of Google’s channels, ensuring comprehensive visibility for the advertiser.
In conclusion, the type of PPC campaign you choose should align with your business objectives, target audience, and the nature of your product or service. Testing different campaigns can also provide insights into what resonates best with your audience.
Types of Bidding Strategies
The bidding strategy determines how you pay for users to interact with your ads. You can opt for strategies like cost-per-click (CPC), cost-per-impression (CPM), or cost-per-acquisition (CPA).
1. Cost-Per-Click (CPC) Bidding
Description: You pay each time someone clicks on your ad. This is the most common bidding strategy, especially for search campaigns.
Best for: Campaigns focused on driving website traffic.
2. Cost-Per-Impression (CPM) Bidding
Description: With CPM bidding, you pay for every 1,000 times your display or video ad is shown (not when it’s clicked).
Best for: Brand awareness campaigns where the focus is on maximizing exposure.
3. Cost-Per-Acquisition (CPA) Bidding
Description: You set a target CPA, and the system automatically sets your bids to get as many conversions as possible at that target.
Best for: Campaigns with a primary goal of driving conversions, like form submissions or sales.
4. Enhanced Cost-Per-Click (ECPC)
Description: Google automatically adjusts your manual bids to maximize conversions. It can raise your bid if a click seems more likely to lead to a sale or conversion, or lower it if not.
Best for: Advertisers who still want some control over their CPC bids but also want to optimize for conversions.
5. Maximize Clicks
Description: An automated bid strategy that sets your bids to help get as many clicks as possible within your budget.
Best for: Businesses looking to maximize website traffic.
6. Maximize Conversions
Description: Google automatically sets bids to help you get the most conversions for your campaign while spending your budget.
Best for: Campaigns with a primary goal of driving conversions and have flexible budgets.
7. Target Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
Description: You set a target return on ad spend, and Google sets your bids to maximize conversion value based on that return.
Best for: Campaigns focused on achieving a specific return for every dollar spent on ads.
8. Portfolio Bidding
Description: This is a set of automated bid strategies that you can apply across multiple campaigns, ad groups, and keywords.
Best for: Advertisers running multiple campaigns who want to apply a consistent bidding strategy across them.
9. Shared Budgets
Description: Instead of setting individual budgets for each campaign, you allocate a shared pool of money to a set of campaigns.
Best for: Advertisers managing several campaigns who want flexibility in how money is spent based on performance.
In conclusion, selecting the right bidding strategy is pivotal to your PPC campaign’s success. By aligning your bidding strategy with your campaign goals, you can drive the desired results while optimizing your ad spend. Regularly reviewing and tweaking your bidding strategy can also lead to improved performance over time.
Keyword Research
This is where you find and analyze search terms that people enter into search engines. The insight you get from these keyword searches can help drive your PPC strategy.
Keyword research is the process of identifying words and phrases that potential customers use in search engines. The goal is to find terms that can drive qualified traffic to your website or landing page through PPC ads.
Importance of Keyword Research
1. Understanding Your Audience
By identifying the keywords your audience uses, you gain insights into their needs, preferences, and pain points.
2. Budget Allocation
By focusing on the right keywords, you ensure a more efficient use of your PPC budget.
3. Higher Conversion Rates
Proper keyword selection can lead to more relevant traffic and thus higher conversion rates.
Steps to Conducting Keyword Research

Step #1: Brainstorming
Start by listing out terms related to your product or service. Think about what potential customers might type into search engines.
Step #2: Use Keyword Research Tools
Tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Ubersuggest can help expand your list and provide data on keyword volume, competition, and cost-per-click.
Also read – Top 10 Free Keyword Research Tools
Step #3: Look at Competitors
Analyze the keywords your competitors are targeting. This can offer new keyword ideas and give insights into the competitive landscape.
Step #4: Focus on Long-Tail Keywords
These are longer and more specific keyword phrases. Though they often have lower search volumes, they can be less competitive and more targeted, leading to better conversion rates.
Step #5: Analyze Search Intent
Understanding the intent behind a keyword (informational, navigational, transactional, or commercial) can help you tailor your ad copy and landing pages to better meet users’ needs.
Step #6: Group Keywords
Organize your keywords into closely related groups. This can make ad group creation and ad copywriting more manageable and more effective.
Step #7: Regularly Review and Refine
The digital landscape is dynamic. New trends, products, and user behaviors mean that keyword popularity can shift. Regularly reviewing and updating your keyword list ensures that your PPC campaigns remain relevant and effective.
Step #8: Consider Negative Keywords
Negative keywords are terms for which you don’t want your ads to show. By setting negative keywords, you can prevent wasteful ad spend on irrelevant searches.
Tips for Effective Keyword Research
Tip #1. Think Like Your Customer
Put yourself in your customer’s shoes. What terms might they use to find your product or service?
Tip #2. Consider Local Terminologies
If you’re targeting specific regions, consider local slang, terminologies, or alternate spellings.
Tip #3. Stay Updated on Industry Trends
New terms can emerge as industries evolve. Stay updated to capitalize on these new keyword opportunities.
Keyword research isn’t a one-time activity; it’s an ongoing process of refinement and discovery. As you gather data from your campaigns, you’ll gain insights that can guide further optimization. By dedicating time and effort to thorough keyword research, you lay a solid foundation for PPC campaign success.
Ad Copies in PPC Campaign
An ad copy refers to the main text of a clickable advertisement. Whether it’s a search ad appearing on Google or a banner ad on a display network, the copy is the message that conveys the value proposition and call to action to potential customers.
Importance of a Strong Ad Copy
1. First Impressions Matter
For many potential customers, the ad copy might be their first interaction with your brand. A well-crafted message can establish a positive initial impression.
2. CTR and Campaign Performance
A compelling ad copy can increase click-through rates (CTR), directly affecting your ad’s performance and ROI.
3. Relevance to the Audience
Relevant ad copies ensure that the traffic you get is qualified, leading to better conversion rates.
Elements of an Effective Ad Copy

Element #1: Headline
It’s the first thing users notice. Make it attention-grabbing and relevant to the keyword/search query.
Element #2: Description
This elaborates on the headline’s promise. It should provide additional information and highlight benefits or unique selling points.
Element #3: Display URL
While it’s technically part of the ad’s structure, optimizing the URL to include keywords can enhance perceived relevance.
Element #4: Call to Action (CTA)
Directly instructs users on what to do next – whether it’s “Buy Now,” “Learn More,” or “Sign Up.”
Tips for Crafting Compelling Ad Copies
Tip #1: Know Your Audience
Understand their needs, pain points, and desires. Tailor your ad copy to address them.
Tip #2: Highlight Unique Selling Points (USP)
What makes your offering different or superior? It could be free shipping, a discount, high quality, etc.
Tip #3: Use Emotional Triggers

Emotions can drive actions. Whether it’s the joy of a discount, the fear of missing out, or the relief from a solution, tap into emotions.
Tip #4: Stay Relevant

Ensure your ad copy aligns with the keyword, ad group, and the landing page it directs to.
Tip #4: Test and Optimize
Continuously test various ad copies to see what resonates best with your audience. A/B testing can be particularly effective.
Tip #5: Stay Within Character Limits
Search platforms have strict character limits for each ad component. Ensure your message fits without being cut off.
Tip #6: Use Numbers and Symbols
They can make your ad stand out. For example, “Save 50% Today!” can be more eye-catching than “Half off today.”
Tip #7: Implement Ad Extensions (if using platforms like Google Ads)
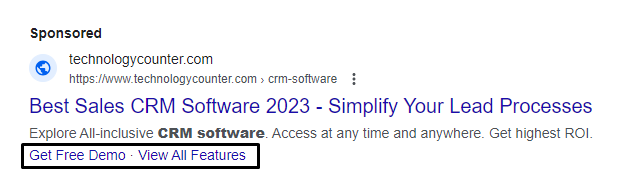
They provide additional information and can significantly improve CTR.
Tip #8: Regular Review and Refresh
The digital landscape is dynamic, and audience preferences can change. Regularly review the performance of your ad copies. If they start underperforming, it might be time for a refresh.
Tip #9: Targeting
Targeting allows you to choose specific attributes or interests of users who will see your ads. This includes keyword targeting, demographic targeting, interest targeting, and retargeting.
Tip #10: Landing Page
This is the page a user lands on after clicking your ad. It should be relevant to the ad copy and optimized for conversions.
Quality Score and Its Factors
Quality Score is Google’s rating of the quality and relevance of your keywords, landing pages, and PPC ads. Higher Quality Scores can lead to lower costs and better ad positions.
What is Quality Score?
Quality Score is a metric used by search engines, particularly Google Ads, to gauge the relevance and quality of your PPC ads and keywords. It’s a rating on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the best possible score.
Why is Quality Score Important?
1. Ad Position
A higher Quality Score can lead to your ads being displayed in better positions on the search engine results page (SERP).
2. Cost Per Click (CPC)
A better Quality Score can lower the cost per click for your ads. Essentially, search engines reward advertisers for relevance and quality with reduced costs.
3. Cost Per Conversion
With a more relevant ad (reflected by a higher Quality Score), you’re more likely to attract users who are genuinely interested in your offering, leading to potentially lower cost per conversion.
Factors Influencing Quality Score
Factor 1: Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Arguably the most influential factor, CTR indicates how relevant users find your ad based on the keyword they searched for. A higher CTR generally leads to a better Quality Score.
Factor 2: Relevance of Keyword to Ad Group
How closely related is your chosen keyword to the other keywords in its ad group? Tighter, more relevant groupings are favorable.
Factor 3: Landing Page Quality
After clicking on your ad, users are directed to a landing page. Search engines assess the quality, relevance, and overall user experience of this page. Factors include content relevance, navigation ease, load time, and mobile optimization.
Factor #4: Ad Text Relevance
How well does your ad copy relate to the keyword it’s tied to? Users should be able to draw a clear connection between their search query and your ad.
Factor #5: Historical Google Ads Account Performance
If you’ve consistently offered high-quality, relevant ads, your account’s historical performance could benefit your Quality Score.
How to Improve Quality Score
Tip #1: Enhance CTR
Tweaking your ad copy to make it more compelling and relevant can lead to improved click-through rates.
Tip #2: Optimize Landing Pages
Ensure that your landing pages are relevant, offer a good user experience, and are optimized for conversions. Additionally, consider the page’s load time and mobile optimization.
Tip #3: Keyword Relevance
Regularly review your keywords. Remove or replace those that aren’t performing well and ensure that your ad groups are tightly themed.
Tip #4: Ad Copy Optimization
As mentioned, relevance is key. Ensure your ad copy aligns with the keywords in its ad group and the landing page it directs to.
Tip #5: Negative Keywords
By specifying which keywords you don’t want your ads to show for, you can prevent irrelevant clicks and improve overall relevance.
Tip #6: Engage in Ad Extensions
Using ad extensions can provide additional information and increase the overall click-through rate, benefiting your Quality Score.
Quality Score isn’t just a number; it’s a reflection of the health and efficiency of your PPC campaigns. While it’s one of several metrics you should keep an eye on, understanding and optimizing for Quality Score can lead to more cost-effective campaigns and better overall performance in the search ad space.
A/B Testing
A/B testing is a method of comparing two versions of a webpage or ad to see which one performs better. You show two variants, A and B, to different segments of your audience at the same time. By analyzing the results, you can determine which variant drives more conversions or achieves your goal more effectively.
Importance of A/B Testing in PPC
A/B testing plays a pivotal role in PPC campaign optimization. Here’s why it’s important:
1. Improves Campaign Performance
By determining which variant performs better, you can optimize your campaigns to drive more clicks, conversions, and revenue.
2. Reduces Ad Spend
A well-optimized ad means you’re getting more out of each click, potentially reducing your cost per click (CPC) and cost per acquisition (CPA).
3. Enhances User Experience
Testing allows you to understand what your audience prefers, helping create a better user experience.
Elements to Test in PPC Campaigns
While you can test almost any element in your campaign, here are some common elements often tested:

Element #1: Ad Copy
Test different headlines, descriptions, and CTAs to see what drives more clicks and conversions.
Element #2: Landing Pages
Experiment with different designs, layouts, copy, and calls-to-action on your landing page.
Element #3: Keywords
You can test the performance of different keywords and keyword match types.
Element #4: Bidding Strategies
Experiment with different bidding strategies to see which gives you the best return on investment.
Element #5: Ad Extensions
Test different types of ad extensions to see which ones improve click-through rates (CTR).
How to Conduct A/B Testing
Below is the brief concise guide on conducting A/B testing
Step #1: Identify What to Test
Decide which element you want to test. It could be a headline, image, CTA, etc.
Step #2: Create Variations
Create a new version of the ad or landing page, changing only the element you’re testing.
Step #3: Split Your Audience
Divide your audience into two segments. Each segment should be exposed to only one version of the ad.
Step #4: Run the Test
Launch both versions of the ad at the same time. Ensure the test runs long enough to gather statistically significant data.
Step #5: Analyze Results
Use analytical tools to determine which version performed better. Look at metrics like CTR, conversion rate, and bounce rate.
Step #6: Implement Changes
Apply the winning element to your ad campaign.
Step #7: Repeat
A/B testing is not a one-time process. It should be done continuously to consistently improve your PPC campaigns.
A/B testing is a powerful method for making data-driven decisions in your PPC campaigns. By continuously testing and tweaking your campaigns, you can improve their performance and ensure you’re getting the best possible return on your ad spend.
Top Tools for PPC
Utilizing the right tools can make a significant difference in the effectiveness and efficiency of your PPC campaigns. From keyword research to competitive analysis, and from ad creation to campaign management, there’s a tool for nearly every PPC task. Here’s a rundown of some top tools used in PPC marketing:
1. Google Keyword Planner
- Function: PPC platform for Google search and display networks.
- Features: Keyword Planner for keyword research, Ad Preview to see how your ads look, and the Google Ads Editor for bulk editing and campaign management.
2. Bing Ads (Microsoft Advertising)
- Function: PPC platform for the Bing search engine.
- Features: Offers tools similar to Google Ads, like a keyword planner and ad preview, but for the Bing network.
3. SEMrush
- Function: Comprehensive digital marketing suite with a focus on competitive analysis.
- Features: Allows users to see competitors’ top keywords, ad copies, and even their budget allocation. Also provides keyword research and position tracking.
4. AHREFs
- Function: Originally a backlink analysis tool, it’s grown into an all-in-one SEO and PPC tool.
- Features: Allows keyword research, competitor analysis, and PPC campaign audits, among other functionalities.
5. WordStream
- Function: PPC management and optimization platform.
- Features: Provides insights on PPC performance, offers suggestions for optimization, and allows for ad creation and editing.
6. Unbounce
- Function: Landing page builder and A/B testing tool.
- Features: Allows marketers to easily create and test different landing page variations to optimize for conversions.
7. Optmyzr
- Function: PPC management and automation tool.
- Features: Automated PPC reports, management of shopping ads, scripts for ad automation, and quality score trackers.
8. AdEspresso
- Function: A platform for Facebook, Instagram, and Google Ads management.
- Features: Simplifies the process of creating, managing, and optimizing ads on these platforms. Also provides analytics and A/B testing capabilities.
9. SpyFu
- Function: Competitive analysis tool.
- Features: Allows you to see your competitors’ most profitable keywords, their ad copies, and their monthly ad spend.
10. Google Analytics
- Function: Web analytics tool.
- Features: While not strictly a PPC tool, Google Analytics is crucial for tracking conversions, understanding user behavior post-click, and assessing the quality of traffic coming from PPC campaigns.
11. Canva
- Function: Graphic design tool.
- Features: Useful for creating display ads or visuals for landing pages without needing advanced graphic design skills.
12. AdRoll
- Function: Retargeting and multi-platform advertising.
- Features: Allows you to retarget users across different platforms and devices, ensuring your brand remains top-of-mind.
The world of PPC is vast and multifaceted. Equipping yourself with the right tools ensures that you can stay competitive, gain valuable insights, and continuously optimize your campaigns for better results. Whether you’re looking to research keywords, build landing pages, analyze competitors, or manage bids, there’s a tool out there that can streamline the process.
Important KPIs for PPC
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are vital metrics used to evaluate the performance and effectiveness of PPC campaigns. Understanding these metrics allows advertisers to optimize campaigns, manage budget allocation, and achieve desired outcomes more effectively. Here’s a deeper dive into some of the most crucial KPIs for PPC:

1. Cost Per Click (CPC)
- Definition: The average amount you pay every time someone clicks on your ad.
- Importance: CPC helps you understand the cost-efficiency of your keywords and campaigns. Monitoring and optimizing CPC ensures you’re not overspending for traffic.
2. Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Definition: The percentage of times your ad is shown (impressions) versus the number of clicks it receives.
- Formula: CTR = (Number of Clicks / Number of Impressions) x 100%
- Importance: A higher CTR indicates your ad copy and keywords are relevant to your target audience. It’s a strong signal for the overall effectiveness and relevance of your ad.
3. Cost Per Acquisition (CPA)
- Definition: The average cost to acquire one lead, sign-up, purchase, or whatever conversion action you’ve defined.
- Importance: CPA provides insights into the cost-effectiveness of your campaigns. If CPA is too high, it may indicate issues with either the CPC, conversion rate, or both.
4. Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
- Definition: A metric that indicates the revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising.
- Formula: ROAS = (Revenue from Ad Campaign / Cost of Ad Campaign)
- Importance: ROAS helps you evaluate the profitability of your ad campaigns. A ROAS greater than 1 indicates a positive return, while anything less than 1 means you’re not breaking even.
5. Conversion Rate (CVR)
- Definition: The percentage of clicks that result in a conversion (e.g., a sale, sign-up, lead, etc.).
- Formula: CVR = (Number of Conversions / Number of Clicks) x 100%
- Importance: CVR tells you how effective your ad and landing page are at converting traffic. A low CVR may indicate misalignment between the ad copy and the landing page or a poor user experience.
6. Quality Score
- Definition: A metric (on a scale from 1 to 10) used by platforms like Google Ads to assess the relevance and quality of your PPC ads and keywords.
- Importance: A better Quality Score can lead to reduced CPC and better ad positions.
7. Ad Position
- Definition: The placement of your ad on the search engine results page (SERP). For instance, an ad position of 1 means your ad is the first listed ad.
- Importance: Higher positions usually result in higher visibility and click-through rates. However, top positions might come with higher CPCs.
8. Impression Share
- Definition: The percentage of impressions your ad received compared to the total number it was eligible to get.
- Importance: This metric can show market potential and whether you’re missing out on potential visibility due to budget constraints or low ad rank.
Understanding and monitoring these KPIs provides insights into the health, effectiveness, and areas of improvement for your PPC campaigns. Continuous tracking and optimization based on these metrics will ensure that your campaigns remain cost-effective and goal-oriented.
Myths about PPC
As with any digital marketing strategy, PPC (Pay-Per-Click) is surrounded by its fair share of myths and misconceptions. These can lead to poor decision-making or missed opportunities for businesses. Here are some of the most common myths about PPC, along with clarifications:

Myth #1: Setting Up PPC Campaigns Is Easy; Just Add Keywords and Ads
- Reality: While platforms like Google Ads are user-friendly, creating a successful PPC campaign requires research, strategy, and continuous optimization. Merely setting and forgetting can result in wasted ad spend.
Myth #2: High Traffic Means High Success
- Reality: High traffic to your website is good, but if those clicks aren’t converting into sales or leads, you may just be wasting money. A successful PPC campaign focuses on both quantity and quality of traffic.
Myth #3: Being #1 on Ads Is the Best Position
- Reality: While being in the top spot can lead to more clicks, it also usually comes with a higher cost per click (CPC). Sometimes, being in the 2nd or 3rd position provides a better ROI, depending on the competitiveness of the keywords and the industry.
Myth #4: PPC Is Too Expensive for Small Businesses
- Reality: With the right strategy, any business can benefit from PPC. You can set your budgets, target specific regions, and pause campaigns anytime, giving small businesses ample control over their spending.
Myth #5: PPC Affects Organic Search Rankings
- Reality: PPC and SEO (organic search) are two separate entities. Spending on PPC won’t improve your organic ranking, nor will high organic rankings reduce your PPC costs.
Myth #6: If You Stop PPC, You’ll Maintain the Same Sales Volume
- Reality: PPC drives additional traffic to your site, which can lead to increased sales. When you stop PPC campaigns, you’ll likely see a decrease in traffic and, consequently, sales or leads.
Myth #7: Negative Keywords Aren’t Important
- Reality: Negative keywords help prevent your ads from being triggered by irrelevant search terms, ensuring better targeting and potentially saving significant amounts on wasted clicks.
Myth #8: PPC Only Works for E-commerce or B2C Companies
- Reality: While e-commerce businesses often benefit from PPC, B2B companies can also utilize PPC effectively, especially with platforms like LinkedIn Ads which cater specifically to professional audiences.
Myth #9: Once Set Up, PPC Campaigns Don’t Require Monitoring
- Reality: Continuous monitoring and optimization are crucial for the success of PPC campaigns. Regularly reviewing and adjusting bids, ad copy, and targeting can significantly improve results.
Myth #10: Broad Match Keywords Are Enough
- Reality: Relying solely on broad match keywords can result in your ads being triggered for irrelevant searches. It’s often best to use a mix of match types, including phrase match and exact match, for better targeting.
Myths about PPC can lead businesses astray, resulting in inefficiencies, wasted budgets, or missed opportunities. It’s crucial to understand the realities of PPC marketing and to continually educate oneself, especially given the dynamic nature of digital advertising.
Remember, PPC marketing is a journey that requires a continuous learning and tweaking approach. Mastering it can offer significant benefits and contribute to your business growth. In case you are in need of expert PPC services for your business, do not hesitate to reach our Web Zodiac.


0 Comments